Understanding Cosine Similarity

Cosine similarity is used to measure how similar things are. Mathematically, it's a measure of similarity between two vectors. Cosine similarity is widely used in Machine Learning and Data Science, particularly when measuring similarity between vectors projected in a multidimensional space.
The formula for Cosine similarity for two vectors A and B is:
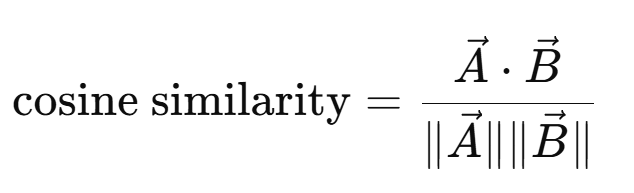
Let's go through a worked example.
Worked Example of Calculating Cosine Similarity
Let's assume we have the following vectors A and B:
A = [ 2, 7, 9, 12 ]
B = [ 1, 3, 16, 21 ]
Step 1 - Calculate the dot product of Vectors A and B
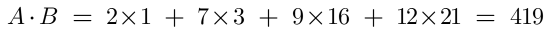
Step 2 - Calculate the magnitude of Vectors A and B
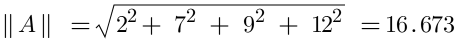
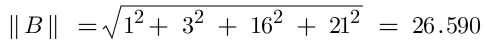
Step 3 - Calculate the Cosine similarity
The cosine can be calculated by dividing the dot product by the magnitude.
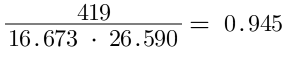
The cosine similarity is 0.945. This indicates a high similarity between vectors A and B (meaning A and B are pointing in a similar direction in 4D space).
Calculating Cosine Similarity in R
The lsa package in R provides a cosine function that can be used to calculate the cosine similarity between vectors in R.
library(lsa)
# Define vectors a and b
a <- c(2, 7, 9, 12)
b <- c(1, 3, 16, 21)
# Calculate cosine similarity and display results
print(cosine(a, b))